A growing number of women are becoming aware of the possibility of improving vaginal tone, functionality, and thus their quality of life with minimally invasive procedures.
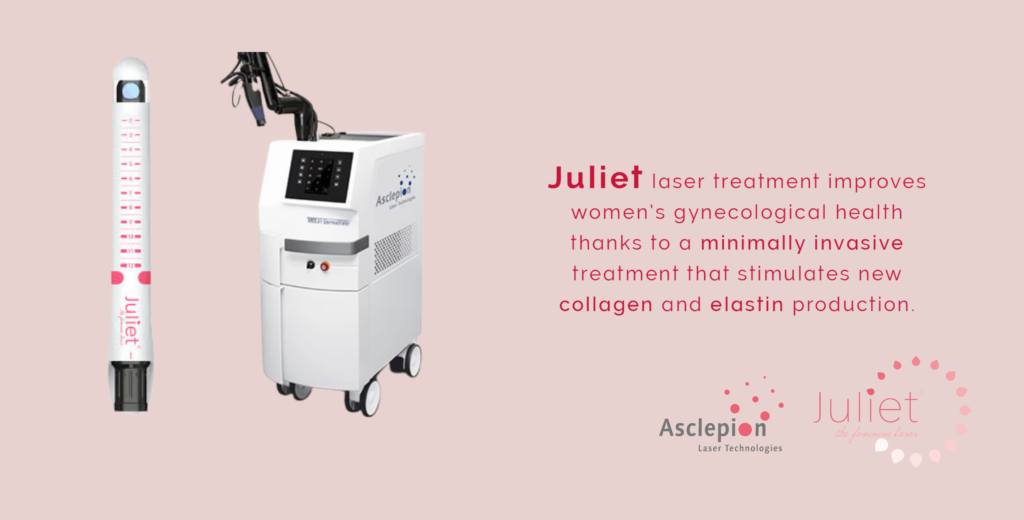
Juliet laser treatment is performed using an Erbium:YAG laser, made by Asclepion, a German company, and represents a fast, gentle, and discreet treatment with a very low risk of side
and minimal downtime.
The primary mechanism of action of Erbium:YAG technology is to achieve the selective stimulation of sub-mucosal collagen, improving the tissue and restoring its original metabolism. This can help to reverse the effects often associated with vaginal laxity, vaginal atrophy, and stress urinary incontinence (SUI).
Due to the adjustable pulse width and peak power, the Erbium:YAG wavelength is the best option for selective heating of target layers (sub-mucosa) and avoiding unwanted effects on surrounding tissues (e.g. muscles or adventitia).
What is Erbium:YAG technology?
Er:YAG lasers have been used for cosmetic and dermatologic procedures since 1996, when the FDA first approved them. A trial comparing Er:YAG to CO2 lasers showed that Er:YAG has equal efficacy, with less side effects and a slight trend toward more rapid recovery.
Initially, short pulse (SP) ER:YAG lasers were approved with pulse lengths of 250-350 microseconds. However, variable and longer-pulse (LP) Er:YAG lasers with pulse lengths of 500 microseconds to 10 milliseconds were subsequently approved in 1999.
The long-pulse and variable-pulse lasers introduced in 1999 were designed to provide enhanced coagulation ability, reducing the side effects of bleeding, which occurred with shorter pulse Er:YAG treatment.
The Er:YAG laser emits a 2940 nm wavelength, which is closest to the absorption peak of water at 3000 nm. When an Er:YAG laser pulse is applied, the flashlamp-pumped crystal laser emits light, which is absorbed by water in the epidermis and papillary dermis. The water vaporises, resulting in a skin-peeling effect in the epidermal layer. Thermal injury in the dermis stimulates collagen production, increased quantities of which can significantly improve the appearance of photodamaged skin while reducing visible rhytids and scars.
Thus, Er: YAG lasers lead to a superficial ablation with the most significant energy absorption in the epidermis and papillary dermis. Furthermore, the vaporisation of water produces a cooling effect, which decreases the amount of heat and damages the surrounding tissues. This cooling allows Er:YAG lasers to be passed over the same skin and ablation area multiple times during the same treatment session without resulting in significant thermal damage and allowing for improved results with fewer treatment sessions.

Why Asclepion Er:YAG 2940 nm laser, quickly became one of the most popular systems for laser vaginal rejuvenation in the world
Fractional vaginal rejuvenation is a simple outpatient procedure that requires no anaesthesia. This technology has been used to treat the syndrome of vaginal relaxation, stress urinary incontinence, and vaginal atrophy. The rehabilitation period after vaginal rejuvenation with an erbium laser is 72 hours.
In 2010, the first clinical study was conducted to use a novel infrared Er:YAG laser technology for treating vaginal laxity and pelvic organ prolapse. Using this laser in conjunction with collagen injection therapy showed great promise for treating these conditions.
From 2010 to 2014, several clinical studies using all four indications were conducted to prove the efficacy and safety of this novel technology. Juliet, the infrared erbium (Er:YAG) laser has an emission wavelength of 2.94 µm and operates in pulse mode. The primary mechanism of action of the laser technology is selective stimulation of the submucosal (lamina propria) collagen synthesis and thermal stimulation of mucosal tissue. An instantaneous contraction reaction in the collagen fibres and acceleration of neocollagenesis leads to the contraction of tissues and an increase in elasticity. Human tissues are a good target for this wavelength because of their very high percentage of water, especially in the vaginal area where mucous membranes are present and in the lamina propria (submucosal area).
The pelvic floor is a complex structure that supports the bladder, uterus, and rectum. The endopelvic fascia is the most critical component of the pelvic floor supportive structures—it contains about 80% of the protein content of this system. Collagen provides tensile strength and integrity, while elastin is responsible for the elasticity and resilience of connective tissue on the pelvic floor.
The extracellular matrix of the vaginal wall consists of collagen type I, III, and V. The ratio of collagen type I / type III, determines the mechanical properties of the vaginal wall. A change in this ratio toward collagen type III can significantly reduce the elasticity of the vaginal wall.
Collagen type V is an essential component of basement membranes. Changes in this collagen are very rare; elastin helps support the pelvic floor. With age, decreased elastin in the extracellular matrix causes loss of submucosal supporting function of the vaginal wall.
Pelvic tissue from women with stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse shows a genetic predisposition to abnormal extracellular matrix remodelling, modulated by reproductive hormones, trauma, mechanical stress load, and aging. This progressive remodelling contributes to stress urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse by altering normal tissue architecture and mechanical properties. Laser-mediated mechanical and heat pulsing of the endopelvic fascia and pelvic floor tissue could be an effective nonsurgical method for treating female urinary incontinence and other disorders resulting from diminished pelvic floor support.
Vaginal Relaxation Syndrome (VRS) & Stress Urinary Incontinence
A common condition usually associated with vaginal childbirth and natural ageing is Vaginal Relaxation Syndrome (VRS), a condition described as a loss of optimal vaginal structure. Pregnancies and births contribute to worsening the VRS condition and the onset of menopause, which causes a decline in hormone levels and vaginal atrophy. This reduces friction during intercourse, leading to a decrease or loss of sexual pleasure.
Stress urinary incontinence is quite common in women after their first birth (24-29% of women suffer from this condition). It is a form of urinary incontinence caused by loss of support of the urethra, usually due to damage to pelvic support structures due to childbirth or frequent exercise in high-impact activities.
Until recently, these conditions were considered an inevitable consequence of female ageing, and treatments were undergone only in rare cases. The traditional surgical treatment represents a very invasive solution to these problems, with high risks of side effects, including wound disruption, dyspareunia, postoperative bleeding, or fistula formation.
Juliet has revolutionised this, representing a fast, virtually painless, minimally invasive treatment with very low risks of side effects and minimal downtime.
Introducing a MCL31 laser, Juliet treatment
Juliet is a non-invasive procedure, that utilises benefits of Er:YAG laser technology and carefully designed and delivered train of laser pulses, to treat vaginal wall tissue. It can be performed by a gynaecologist or a medical practitioner in medical practice, and it takes less than 15 minutes. The treatment does not require incisions or sutures and can be performed on an outpatient basis. Juliet has been proven reliable and effective in treating vaginal laxity, and it is one of the most successful treatments available for this condition.
How does MCL31, Juliet work?
Juliet works by stimulating cellular metabolism and increasing blood flow, causing collagen production in the vaginal tissue. This action continues its beneficial effect even after the treatment has finished and can be observed immediately after the first treatment. The inner mucosa regains elasticity and lubrication, gaining thickness and softness. Itching, irritation, and pain during intercourse disappear due to their stimulating action on the mucosa. Only one to two treatments arenecessary to ensure lasting results.
Juliet is an excellent option for treating various issues, including vaginal dryness, vaginal pain during intercourse and itchiness. It is safe and has minimal complication risks.

Are there any side effects from the Juliet treatment?
The most common side effects include an increase in temperature and low-grade fever on the first day following treatment and odourless vaginal secretions, including spotting. These effects are temporary and usually disappear within one or two days, and some minimal vaginal bleeding or spotting can occur immediately post-treatment.
The healing times are very short, typically no longer than three days. During this time, some secretion may be noticed (pink coloured for the first day, then white coloured). This is a normal reaction and will disappear in a few days.
MCL31 Juliet, the future in women’s vaginal and sexual health treatments
Juliet has a clinical edge over other professional devices currently on the market. The device has numerous advantages, including an excellent safety profile and a gentle delivery mechanism.
Juliet is a revolutionary treatment that has been proven successful in treating vaginal laxity alongside various issues, including vaginal dryness, vaginal pain during intercourse and itchiness.
Backed by extensive clinical research, it is no surprise that Juliet is one of the most sought-after treatment to address vaginal laxity on the market today.
Contact Device Consulting today for more information or to book a complimentary demonstration with one of our product specialists.
Contact UsOr download the MCL31 Juliet information brochure here.
